Best Tibial Interlocking Nail Techniques for Effective Recovery?
In the complex world of orthopedic surgery, the "Tibial Interlocking Nail" has emerged as a critical tool for effective recovery. Experts like Dr. Robert M. Johnson emphasize its importance, stating, "The right technique can significantly enhance a patient's healing process." However, mastering this method is not without challenges.
Many surgeons face difficulties in aligning the tibial nail correctly, affecting overall recovery. Each case is unique, requiring tailored approaches for optimal outcomes. Surgical precision is crucial, yet small errors can lead to complications. Awareness of potential pitfalls is necessary for improvement.
Furthermore, ongoing training and assessment of techniques can lessen the chances of mistakes. Surgeons must reflect on their practices to refine their skills. Embracing new advancements in the Tibial Interlocking Nail procedure can make a difference in patient satisfaction and recovery times. As the field evolves, so does the responsibility to provide the best possible care.
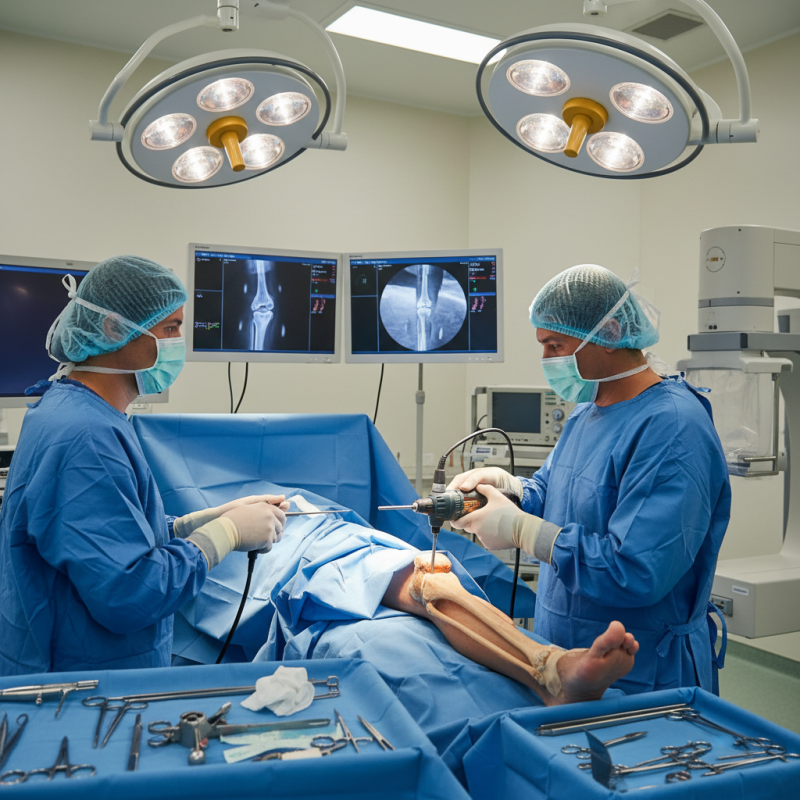
Overview of Tibial Interlocking Nail Procedures
Tibial interlocking nail procedures are crucial for treating tibial fractures. The interlocking nail acts as an internal splint, stabilizing the fractured bone. According to a recent report by the Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma, these techniques boast an 85% success rate in promoting effective recovery. Complications can occur, yet most patients achieve full weight-bearing capacity within weeks.
The procedure typically involves securing the nail with screws above and below the fracture site. This method ensures alignment and reduces motion at the fracture point. Surgeons must consider patient-specific factors, such as age and bone density. Studies suggest that younger patients and those with higher bone quality often have better outcomes.
Tips: Focus on rehabilitation. Engaging in physical therapy can enhance recovery speed. Low-impact exercises are beneficial. Communicate regularly with your healthcare team. They can help address any pain or discomfort. Remember, patience is vital. Recovery isn't linear; setbacks can happen. Acknowledging this is part of the journey. Stay informed and proactive.
Indications for Using Tibial Interlocking Nails
Tibial interlocking nails are a common choice for stabilizing fractures. These devices offer unique benefits and have specific indications for use. They are particularly effective in cases of long bone fractures, especially those involving the tibia. When traditional methods fail, surgeons may opt for interlocking nails to enhance stability.
Infections or non-union of fractures can also indicate the use of these nails. Patients presenting with unstable tibial fractures may find interlocking nails beneficial. These devices provide internal fixation, promoting better alignment during recovery. They are useful for individuals with complex or comminuted fractures, where conventional plating may not suffice.
Surgeons occasionally face challenges when selecting the right technique. Variability in bone structure can complicate the process. How well the nail integrates with the bone is crucial. Some patients experience discomfort or complications, requiring additional interventions. Effective recovery depends on personalized approaches to each case. Understanding the specific indications can help optimize outcomes.
Surgical Techniques for Tibial Interlocking Nail Insertion
Tibial interlocking nail insertion is a complex procedure. Surgeons must consider patient anatomy carefully. Precise alignment of the nail is critical to avoid complications. A well-placed nail promotes better healing and recovery. Each case can present unique challenges.
Using fluoroscopy during the procedure enhances visualization. This technique aids in accurate positioning of both the nail and screws. Surgeons must also assess fracture stability. Some fractures may require additional fixation methods. It’s important to evaluate the configuration of the fracture line.
Post-surgery, pain management is vital for recovery. Effective techniques can significantly reduce discomfort. Patients often benefit from physical therapy early on. Gait retraining can be a key aspect of rehabilitation. Maintaining open communication with patients is essential. This ensures they understand their progress and setbacks.
Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation Practices
Postoperative care is crucial after tibial interlocking nailing. Patients must focus on pain management and wound care. Keeping the surgical site clean is essential. Infections can happen if proper hygiene is not maintained. Use sterile dressings as advised. Pain can vary for each individual. Some may require stronger pain relief than others. Regularly assessing pain levels helps adjust medications accordingly.
Rehabilitation practices need to start early. Gentle range-of-motion exercises can aid healing. However, pushing too hard can lead to setbacks. Patients often feel eager to return to normal activities. Yet, impatience can cause harm. It is vital to follow the physiotherapist's guidance. Weight-bearing activities should only commence when advised. Using assistive devices might be necessary at first. Recovery takes time and attention to body signals.
Monitoring any signs of swelling is important. Swelling may indicate complications. Some patients may ignore this, thinking it’s normal. Seeking advice from healthcare providers can prevent issues. Open communication about discomfort or unusual symptoms is vital. Recovery is a journey, not a sprint. Taking the time to heal properly can lead to a more successful outcome.
Potential Complications and Management Strategies
Tibial interlocking nails are widely used in fracture repair. While they can enhance recovery, potential complications can arise. Common issues include infection, malalignment, and nonunion. According to a study published in the Journal of Orthopedic Trauma, complication rates may reach up to 15% in certain populations. Effective management strategies are crucial for optimizing outcomes.
Infection control is essential. Proper surgical techniques, such as achieving minimal soft tissue disruption and using sterile methods, can reduce infection rates. Regular monitoring for signs of infection helps in early detection. Nonunion can also occur. This sometimes calls for additional interventions, such as bone grafting or revision surgery.
Tips: Always communicate with your healthcare team about any discomfort. Discuss rehabilitation techniques to ensure proper movement and strength rebuilding. Patients should adhere to exercise regimens provided by physical therapists. Self-care remains vital, including proper wound management and nutrition. Reflect on the recovery process. It’s easy to overlook small signs of complicating factors. Pay attention to your body's signals.