How to Use Rapid Prototype Machining for Faster Product Development and Testing
In the fast-paced world of product development, the need for speed and efficiency is paramount. Rapid prototype machining has emerged as a game-changing solution that enables businesses to bring their ideas to life more quickly than ever before. According to Dr. Emily Carter, a leading expert in rapid prototype machining, "The ability to iterate rapidly through prototypes not only shortens the development cycle but also significantly enhances the quality of the final product." This methodology allows engineers and designers to create physical models from digital designs in a matter of days, rather than weeks or months.
The integration of rapid prototype machining in the development process offers numerous advantages, including the ability to test functionality, optimize designs, and gather valuable feedback early on. By harnessing this innovative approach, companies can remain competitive and responsive to market changes. As we explore the principles and practices behind rapid prototype machining, it becomes clear that this technology is not just a trend, but a crucial strategy in achieving faster product development and rigorous testing processes.

Understanding Rapid Prototype Machining in Product Development
Rapid prototype machining is a transformative approach in product development that allows designers and engineers to create accurate models in a fraction of the time typically required. This method leverages advanced machining techniques to quickly produce parts from a variety of materials, enabling teams to iterate designs rapidly. By using computer-aided design (CAD) software, products can be visualized and modified virtually before any physical creation occurs, reducing errors and saving resources.
One of the key advantages of rapid prototype machining is its ability to enhance communication among project stakeholders. As tangible prototypes are developed, they provide a shared reference point, allowing for clearer discussions and more informed decision-making. Feedback can be gathered early in the design process, leading to improved functionality and design fidelity. This iterative cycle of prototyping, testing, and refining accelerates overall project timelines, making it an essential tool for businesses looking to maintain a competitive edge in fast-paced markets.
Rapid Prototype Machining Impact on Product Development Time
This chart illustrates the time allocation across various stages of product development using rapid prototype machining. The data showcases a streamlined approach, highlighting how each stage contributes to overall efficiency.
Benefits of Rapid Prototype Machining for Faster Testing
Rapid prototype machining has revolutionized the product development process by significantly reducing the time and cost associated with testing prototypes. One of the core benefits of this technology is its ability to generate high-precision parts quickly, allowing for iterative testing and refinement. This means that designers can bring their ideas to life in a matter of days rather than weeks, resulting in faster feedback loops and enhanced innovation. Companies can test multiple designs rapidly, making adjustments based on real-world data without committing to expensive manufacturing processes.
When engaging in rapid prototype machining, it's essential to maintain clear communication between design and engineering teams. This facilitates a better understanding of the prototype's purpose and aids in identifying potential design flaws early in the process. Additionally, utilizing Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software effectively can streamline the transition from digital models to physical prototypes.
Tips for successful rapid prototyping include choosing the right materials for the prototypes—considering factors such as durability and functionality. It's also wise to prioritize the most critical features of your product for initial prototypes and focus on those elements during testing. Lastly, always document the testing process thoroughly, as collecting data and insights will inform future iterations and prevent repeated mistakes, ultimately saving both time and resources.
Key Techniques and Technologies in Rapid Prototype Machining
Rapid prototype machining is a game-changer in product development, enabling businesses to create, test, and refine prototypes quickly and efficiently. One of the key techniques in this process is Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining, which allows for precise manufacturing of components based on CAD designs. This technology enables rapid adjustments and iterations, minimizing the time from concept to final product. By using advanced algorithms and high-speed machining centers, teams can achieve tight tolerances and complex geometries essential for modern products.
Another significant technology contributing to rapid prototype machining is 3D printing, which facilitates the creation of intricate prototypes directly from digital models. Methods such as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) and Stereolithography (SLA) provide considerable flexibility in materials and design. These techniques allow for quicker iterations and a broader range of design possibilities, encouraging experimentation and innovation. The combination of CNC machining and 3D printing not only accelerates the prototyping process but also enhances collaboration among development teams as feedback can be integrated in real-time, leading to more successful product outcomes.
How to Use Rapid Prototype Machining for Faster Product Development and Testing - Key Techniques and Technologies in Rapid Prototype Machining
| Technique | Material Used | Typical Applications | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Machining | Aluminum, Plastics | Prototyping Parts, Tooling | High Precision, Fast Turnaround |
| 3D Printing | PLA, ABS, Nylon | Concept Models, Functional Prototypes | Cost-Effective, Complex Geometry |
| Injection Molding | Thermoplastics | High Volume Production, End-use Parts | Fast Production Rate, Consistent Quality |
| Laser Cutting | Metals, Acrylic | Signage, Enclosures | Precise Cuts, Low Waste |
| Thermoforming | PVC, Polyethylene | Packaging, Automotive Parts | Rapid Production, Lightweight Parts |
Integrating Rapid Prototyping into the Product Development Cycle
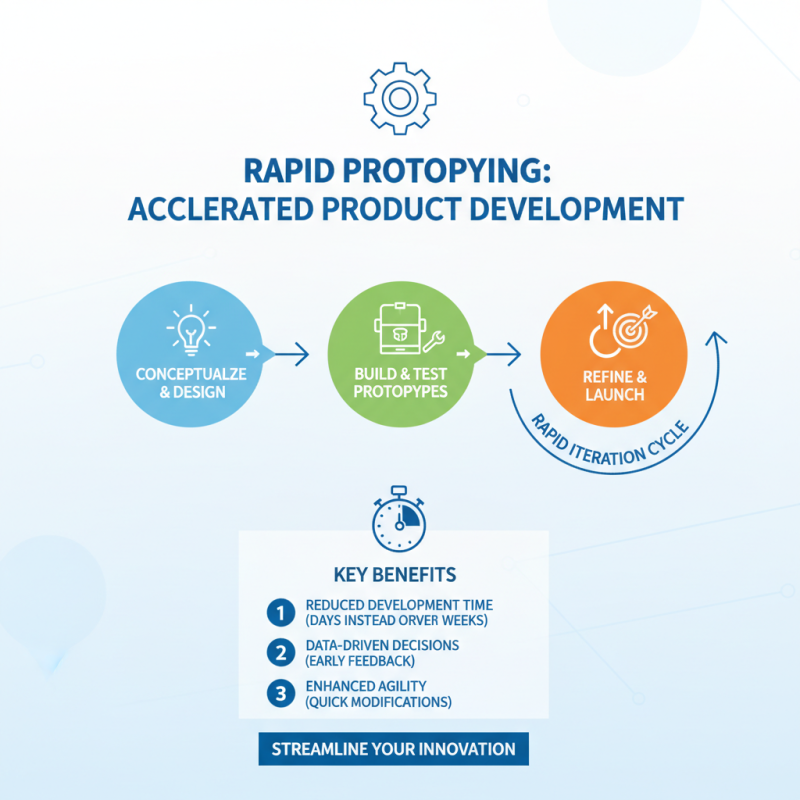
Integrating rapid prototyping into the product development cycle can significantly streamline the processes of design, testing, and iteration. By leveraging rapid prototype machining, teams can quickly transform ideas into tangible models, allowing for real-world testing and feedback. This integration not only reduces development time but also enhances the ability to make data-driven decisions early in the design phase. As prototypes can be produced and modified within a matter of days, this agility is crucial in today's competitive market.
Tips: Consider using various materials during the prototyping phase to test different functionalities and aesthetics. This exploration can reveal design flaws or improvements that might not be apparent in digital models. Additionally, maintain clear communication within the team regarding prototype objectives, as well as any changes made throughout the process. This will ensure that all members are aligned and can contribute valuable insights.
Emphasizing rapid prototypes throughout the development cycle also promotes a culture of innovation. Regular iterations encourage teams to experiment and refine their designs based on both user feedback and performance tests. This practice not only leads to better end products but also fosters collaboration, as diverse perspectives are integrated into each iteration. By embedding rapid prototyping into every stage, companies can stay ahead, adapting quickly to market demands and optimizing product quality.
Best Practices for Effective Rapid Prototype Machining Implementation
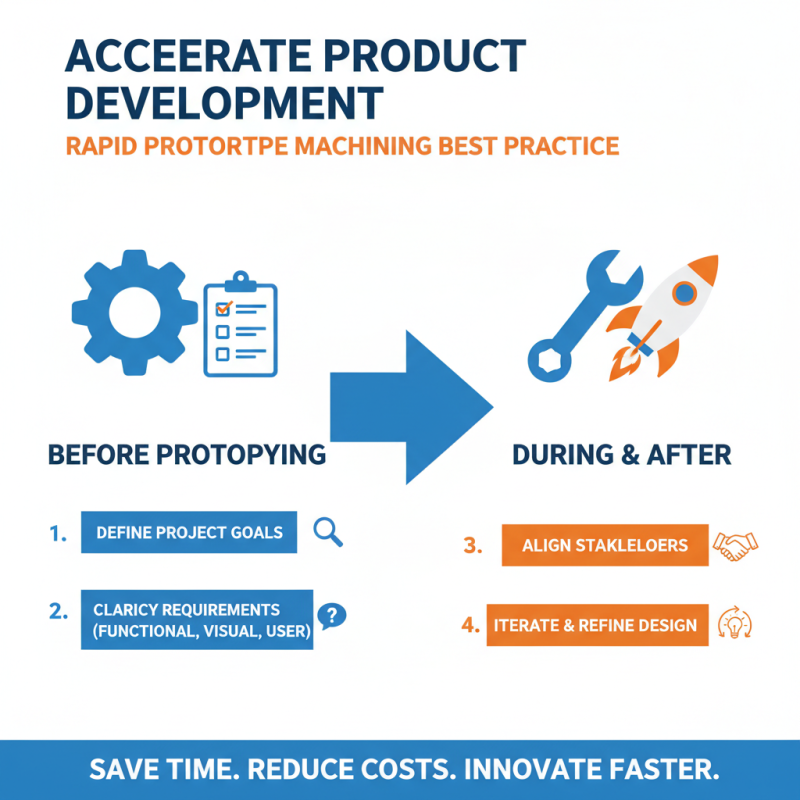
Effective rapid prototype machining is essential for accelerating product development and refining design concepts. One best practice is to clearly define project goals and requirements before initiating the prototyping process. This foundational step ensures that all stakeholders are aligned and that the prototypes produced serve their intended purpose, whether for functional testing, visual inspection, or user feedback. By systematically establishing objectives, designers can prioritize features and make informed decisions about materials and machining methods, avoiding costly revisions later in the development cycle.
Another crucial practice involves selecting the right technology and tools for the specific type of prototype needed. Companies should analyze the intricacies of the design—such as geometric complexity and material specifications—to choose appropriate machining techniques, whether CNC machining, 3D printing, or hybrid approaches. Additionally, implementing an iterative feedback loop during the prototyping phase allows for continuous improvement. Collecting insights from initial tests, incorporating user feedback, and making necessary modifications ensures that the final product closely aligns with user needs and market demands, ultimately leading to a more efficient development process.
Related Posts
-

Understanding the Standards in Best Rapid Prototype Machining Practices
-

China's Premier Rapid Prototype Machining Solutions Powering Global Manufacturing Excellence
-

Exploring CNC Metal Milling Machines at the 138th Canton Fair 2025: Industry Trends and Innovations
-

Unlocking Precision: How Fast CNC Machining Revolutionizes Manufacturing Efficiency by 30%+
-

Challenges Faced by Global Buyers When Sourcing Aluminum CNC Machines
-

Exploring Unique Features and Applications of the Best Rapid CNC Machining Solutions